Mass Spectrometry for precision pharmacology
Quantitative mass spectrometry approaches are used for absolute and relative quantification of lipid mediators and proteins and their modifications. The development of these methods is highly relevant to assessing mediators in disease conditions, thus allowing the development of novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and predictive biomarkers of drug action.
The facility can assess all the lipids of arachidonic acid metabolism called eicosanoids, i.e., prostanoids, leukotrienes, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (also the racemic composition), and phospholipid-esterified eicosanoids in biological samples, such as plasma, serum and urine. Methods are available to assess the enzymatic metabolites of prostanoids in urine as noninvasive markers of prostanoid biosynthesis in vivo. Moreover, the noninvasive markers of oxidative stress are assessed in urine samples by measuring the levels of F2-isoprostanes.
The measurement of these biomarkers in vitro and in vitro allows for defining the mechanism of action of antiinflammatory, antithrombotic, and anticancer agents. It permits the discovery of off-target effects of drugs and toxicity. They can be used in dose-finding studies.
The facility can also assess the pharmacokinetics of drugs by evaluating plasma levels after drug administration.
The facility can assess the absolute quantification (AQUA) of protein expression and post-translational modification. The AQUA method relies on using a synthetic internal standard peptide that is introduced at a known concentration to cell lysates during digestion. Analysis of the proteolyzed sample by a selected reaction monitoring (SRM) experiment in a tandem mass spectrometer results in the direct detection and quantification of both the native peptide and isotope-labeled AQUA internal standard peptide. This strategy has been used to develop quantitative assays to evaluate the acetylation of COX-isozymes by aspirin, which can be used in clinical studies to define aspirin's dose for efficacy and detect aspirin resistance in some clinical settings.
Platform Acquity UPLC (I-CLASS) e spettrometro di massa Xevo TQ-S micro (Waters SpA)
The ACQUITY UPLC Series I-Class System significantly improves the results of complex separations. Compared to systems, typically used for more complex assays, the I-Class series system offers the following advantages:
• Significant reduction of system dispersion
• Fast injection cycles and improved sample yield
These advantages imply the following benefits in comparison to traditional systems:
• Excellent peak capability
• Greater sensitivity
• Faster data acquisition
• Consistent and reproducible results
The I-Class Series System is an effective tool for analyzing complex or diluted samples and offers high resolution and reproducible results for chromatographic separations.
The Waters Xevo TQ-S micro system is an atmospheric pressure ionization (API) triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. It is designed for routine UPLC/MS/MS analysis for quantitative and qualitative applications; thus, it can be used at high acquisition rates typical of UltraPerformance LC technology.
Platform is equipped with MassLynxTM, a powerful software application that configure and controls the platform, and permit to analyze and process the data acquired.
Data are analysed by the facility staff, and the users are provided with files containing the raw data and the complete data analysis.
INFO ACCESS
Because of high specificity and complexity of the platform, it is required the collaboration of the facility Staff (with the know-how and expertise needed to manage and develop mass spectrometry tools) for each application.
For reservation and further information please contact the following email: s.tacconelli@unich.it

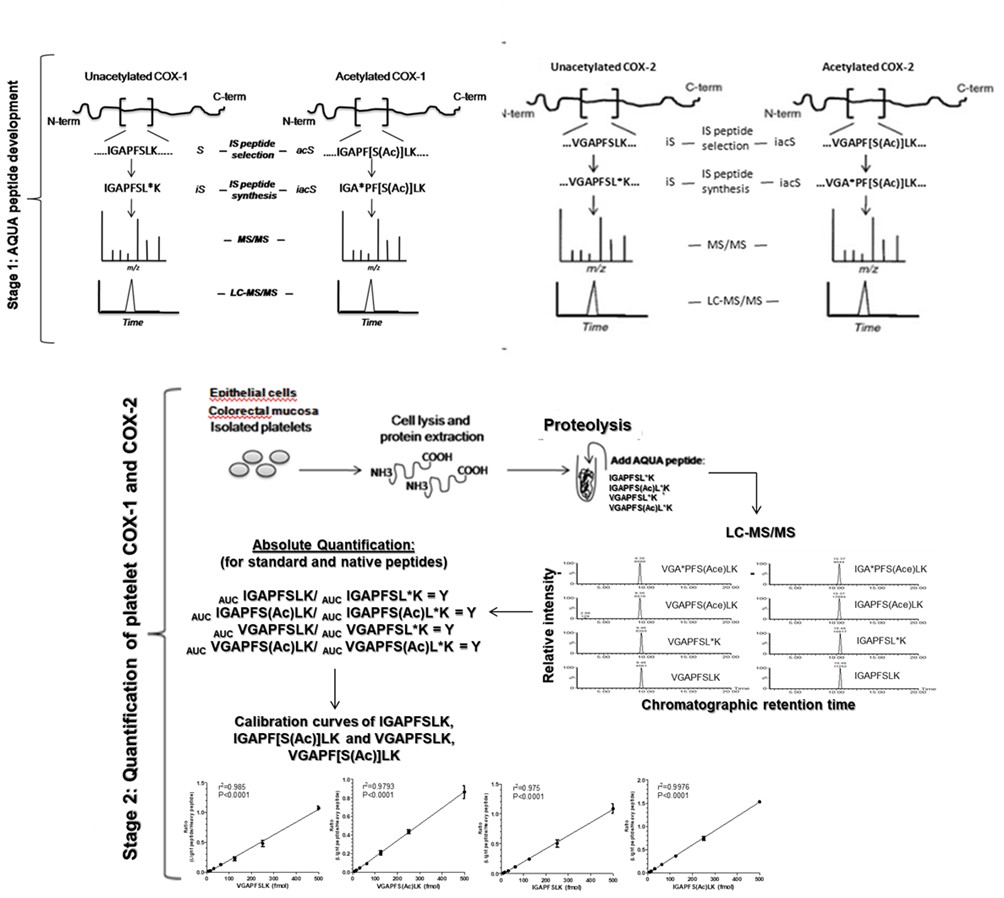
from Patrignani et al., J Thromb Haemost. 2014; Tacconelli et al., Biochem Pharmacol 2020
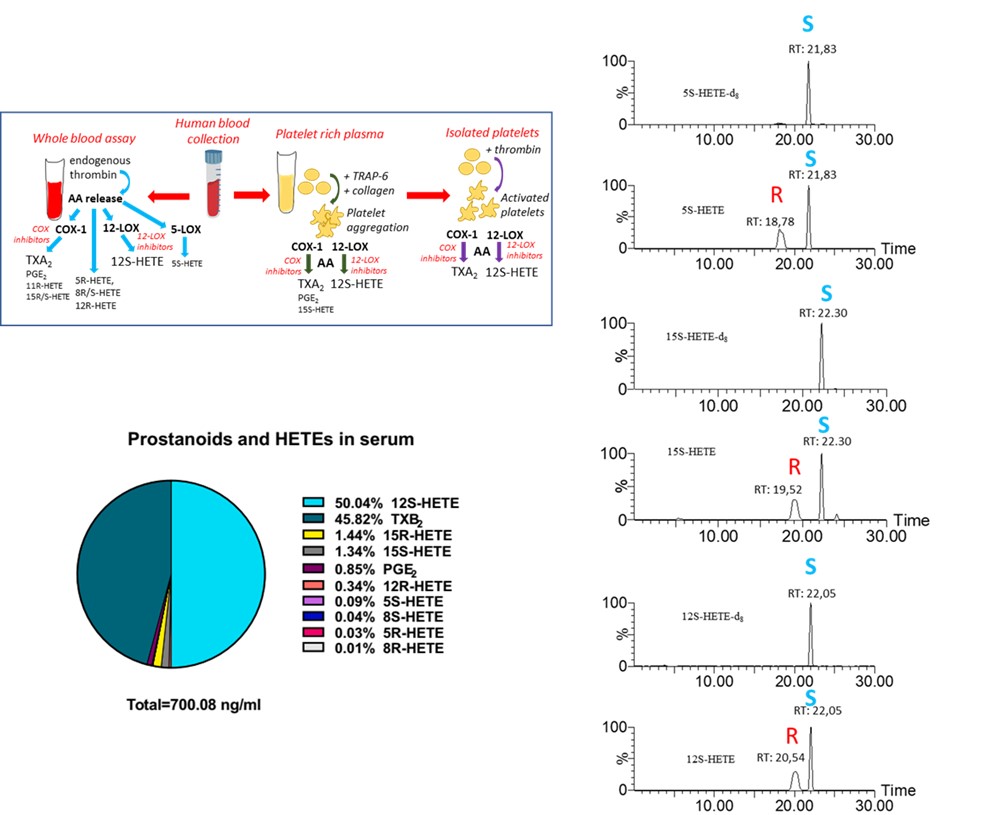
from Tacconelli et al., BBA 2020
- Tacconelli S, Contursi A, Falcone L, Mucci M, D'Agostino I, Fullone R, Sacco A, Zucchelli M, Bruno A, Ballerini P, Dovizio M, Patrignani P. Characterization of cyclooxygenase-2 acetylation and prostanoid inhibition by aspirin in cellular systems. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;178:114094.
- Tacconelli S, Fullone R, Dovizio M, Pizzicoli G, Marschler S, Bruno A, Zucchelli M, Contursi A, Ballerini P, Patrignani P. Pharmacological characterization of the biosynthesis of prostanoids and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids in human whole blood and platelets by targeted chiral lipidomics analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020;1865(12):158804.
- Di Francesco L, Bruno A, Ricciotti E, Tacconelli S, Dovizio M, Guillem-Llobat P, Alisi MA, Garrone B, Coletta I, Mangano G, Milanese C, FitzGerald GA, Patrignani P. Pharmacological characterization of the microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 inhibitor AF3485 in vitro and in vivo. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2020 2;11:374.
- Sacco A, Bruno A, Contursi A, Dovizio M, Tacconelli S, Ricciotti E, Guillem-Llobat P, Salvatore T, Di Francesco L, Fullone R, Ballerini P, Arena V, Alberti S, Liu G, Gong Y, Sgambato A, Patrono C, FitzGerald GA, Yu Y, Patrignani P. Platelet-Specific Deletion of Cyclooxygenase-1 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;370(3):416-426.
- Saul MJ, Baumann I, Bruno A, Emmerich AC, Wellstein J, Ottinger SM, Contursi A, Dovizio M, Donnini S, Tacconelli S, Raouf J, Idborg H, Stein S, Korotkova M, Savai R, Terzuoli E, Sala G, Seeger W, Jakobsson PJ, Patrignani P, Suess B, Steinhilber D. miR-574-5p as RNA decoy for CUGBP1 stimulates human lung tumor growth by mPGES-1 induction. FASEB J. 2019;33(6):6933-6947.
- Tacconelli S, Dovizio M, Di Francesco L, Meneguzzi A, D'Agostino I, Evangelista V, Manarini S, Capone ML, Grossi L, Porreca E, Di Febbo C, Bruno A, Ballerini P, Levantesi G, Fava C, Minuz P, Patrignani P. Reduced variability to aspirin antiplatelet effect by the coadministration of statins in high-risk patients for cardiovascular disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 104(1): 111-119.
- Patrignani P, Sacco A, Sostres C, Bruno A, Dovizio M, Piazuelo E, Di Francesco L, Contursi A, Zucchelli M, Schiavone S, Tacconelli S, Patrono C, Lanas A. Low-dose aspirin acetylates cyclooxygenase-1 in human colorectal mucosa: implications for the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017 02(1):52-61.
- Guillem-Llobat P, Dovizio M, Bruno A, Ricciotti E, Cufino V, Sacco A, Grande R, Alberti S, Arena V, Cirillo M, Patrono C, FitzGerald GA, Steinhilber D, Sgambato A, Patrignani P. Aspirin prevents colorectal cancer metastasis in mice by splitting the crosstalk between platelets and tumor cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(22):32462-77.
- Patrignani P, Tacconelli S, Piazuelo E, Di Francesco L, Dovizio M, Sostres C, Marcantoni E, Guillem-Llobat P, Del Boccio P, Zucchelli M, Patrono C, Lanas A. Reappraisal of the clinical pharmacology of low-dose aspirin by comparing novel direct and traditional indirect biomarkers of drug action. J Thromb Haemost. 2014; 12(8):1320-3.
- Maenthaisong R, Tacconelli S, Sritara P, Del Boccio P, Di Francesco L, Sacchetta P, Archararit N, Aryurachai K, Patrignani P, Suthisisang C. Clinical pharmacology of cyclooxygenase inhibition and pharmacodynamic interaction with aspirin by floctafenine in Thai healthy subjects. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013;26(2):403-17
- Dovizio M, Tacconelli S, Ricciotti E, Bruno A, Maier TJ, Anzellotti P, Di Francesco L, Sala P, Signoroni S, Bertario L, Dixon DA, Lawson JA, Steinhilber D, FitzGerald GA, Patrignani P. Effects of celecoxib on prostanoid biosynthesis and circulating angiogenesis proteins in familial adenomatous polyposis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;341(1):242-50.
- Cesari M, Kritchevsky SB, Nicklas B, Kanaya AM, Patrignani P, Tacconelli S, Tranah GJ, Rognoni G, Harris TB, Antonelli Incalzi R, Newman AB, Pahor M, for the Health ABC study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67A(6):671-676.
- Capone ML, Tacconelli S, Sciulli MG, Anzellotti P, Di Francesco L, Merciaro G, Di Gregorio P, Patrignani P. Human pharmacology of naproxen sodium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007; 322(2): 453-60.
- Sciulli MG, Filabozzi P, Tacconelli S, Padovano R, Ricciotti E, Capone ML, Grana M, Carnevale V, Patrignani P. Platelet activation in patients with colorectal cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005; 72(2): 79-83.
- Minuz P, Patrignani P, Gaino S, Seta F, Capone ML, Tacconelli S, Degan M, Faccini G, Fornasiero A, Talamini G, Tommasoli R, Arosio E, Santonastaso CL, Lechi A, Patrono C. Determinants of platelet activation in human essential hypertension. Hypertension. 2004; 43(1):64-70.
- Capone ML, Tacconelli S, Sciulli MG, Grana M, Ricciotti E, Minuz P, Di Gregorio P, Merciaro G, Patrono C, Patrignani P. Clinical pharmacology of platelet, monocyte, and vascular cyclooxygenase inhibition by naproxen and low-dose aspirin in healthy subjects. Circulation. 2004; 109(12): 1468-71
- Minuz P, Patrignani P, Gaino S, Degan M, Menapace L, Tommasoli R, Seta F, Capone ML, Tacconelli S, Palatresi S, Bencini C, Del Vecchio C, Mansueto G, Arosio E, Santonastaso CL, Lechi A, Morganti A, Patrono C. Increased oxidative stress and platelet activation in patients with hypertension and renovascular disease. Circulation. 2002; 106(22): 2800-5.
- Patrignani P, Panara MR, Tacconelli S, Seta F, Bucciarelli T, Ciabattoni G, Alessandrini P, Mezzetti A, Santini G, Sciulli MG, Cipollone F, Davì G, Gallina P, Bon GB, Patrono C. Effects of vitamin E supplementation on F(2)-isoprostane and thromboxane biosynthesis in healthy cigarette smokers. Circulation. 2000;102(5): 539-45.
-
D'Agostino I, Tacconelli S, Bruno A, Contursi A, Mucci L, Hu X, Xie Y, Chakraborty R, Jain K, Sacco A, Zucchelli M, Landolfi R, Dovizio M, Falcone L, Ballerini P, Hwa J, Patrignani P. Low-dose Aspirin prevents hypertension and cardiac fibrosis when thromboxane A2 is unrestrained. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105744.
-
Contursi A, Schiavone S, Dovizio M, Hinz C, Fullone R, Tacconelli S, Tyrrell VJ, Grande R, Lanuti P, Marchisio M, Zucchelli M, Ballerini P, Lanas A, O’Donnell VB, Patrignani P. Platelets induce free and phospholipid-esterified 12-HETE generation in colon cancer cells by delivering 12-lipoxygenase. J Lipid Res 2021;100109.
-
Bruno A, Contursi A, Tacconelli S, Sacco A, Hofling U, Mucci M, Lamolinara A, Del Pizzo F, Ballerini P, Di Gregorio P, Yu Y, Patrignani P. The specific deletion of cyclooxygenase-1 in megakaryocytes/platelets reduces intestinal polyposis in ApcMin/+ mice. Pharmacol Res. 2022; 185: 106506.
-
Hofling U, Tacconelli S, Contursi A, Bruno A, Mucci M, Ballerini P, Cohen S, Patrignani P. Characterization of the acetylation of cyclooxygenase-isozymes and targeted lipidomics of eicosanoids in serum and colon cancer cells by the new Aspirin formulation IP1867B versus Aspirin in vitro. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2022;13:1070277
-
Lanas A, Tacconelli S, Contursi A, Piazuelo E, Bruno A, Ronci M, Marcone S, Dovizio M, Sopeña F, Falcone L, Milillo C, Mucci M, Ballerini P, Patrignani P. Biomarkers of response to low-dose Aspirin in Familial Ade-nomatous Polyposis patients. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15(9):2457.
-
Patrignani P, Tacconelli S, Contursi A, Piazuelo E, Bruno A, Nobili S, Mazzei M, Milillo C, Hofling U, Hijos-Mallada G, Sostres C, Lanas A. Optimizing aspirin dose for colorectal cancer patients through deep phenotyping using novel biomarkers of drug action. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1362217.
|
|
|

