Experimental Pathology of Resolution (PI Recchiuti)
Workgroup Leader: Dr. Antonio Recchiuti
 |
|
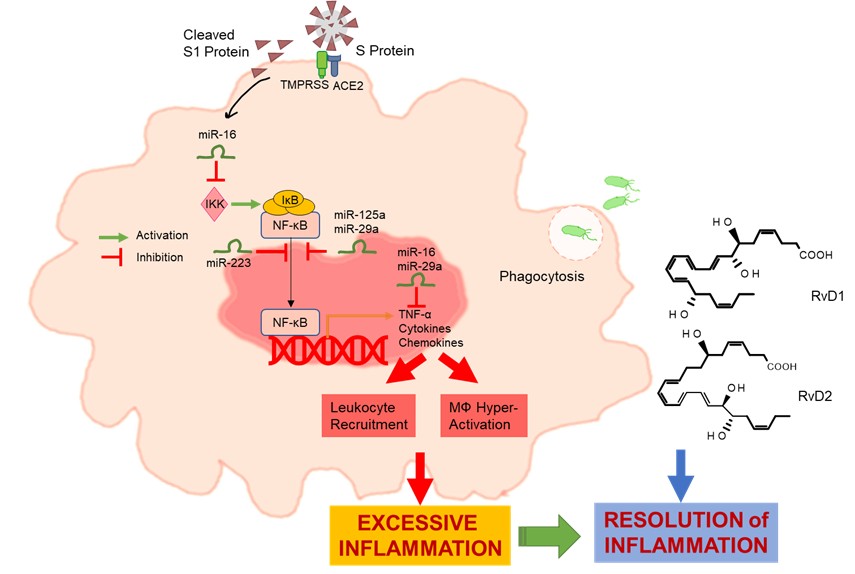
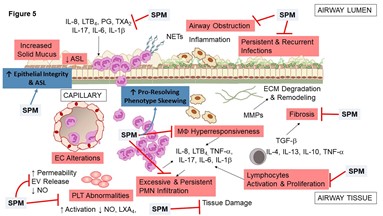
Dr. Recchiuti’s workgroup is interested in determining roles, actions, and therapeutic potential of SPM in cystic fibrosis (CF), in which a defect in SPM pathways can contribute to sustain chronic inflammation and infection. His group has demonstrated that the SPM RvD1 potently reduces inflammation and infection in in vivo and ex vivo models of CF, by acting on macrophage-mediated bacterial and leukocyte clearance and reducing the expression of genes associated with NF-kB activation (Isopi et al., Front. Immunol., 2020). More recently, the research group coordinated by Dr. Recchiuti has uncovered potent anti-inflammatory actions of RvD1 and D2 on macrophages, both from non-CF and CF individuals, exposed to SARS-CoV-2 proteins (Recchiuti et al., Faseb J., 2021).
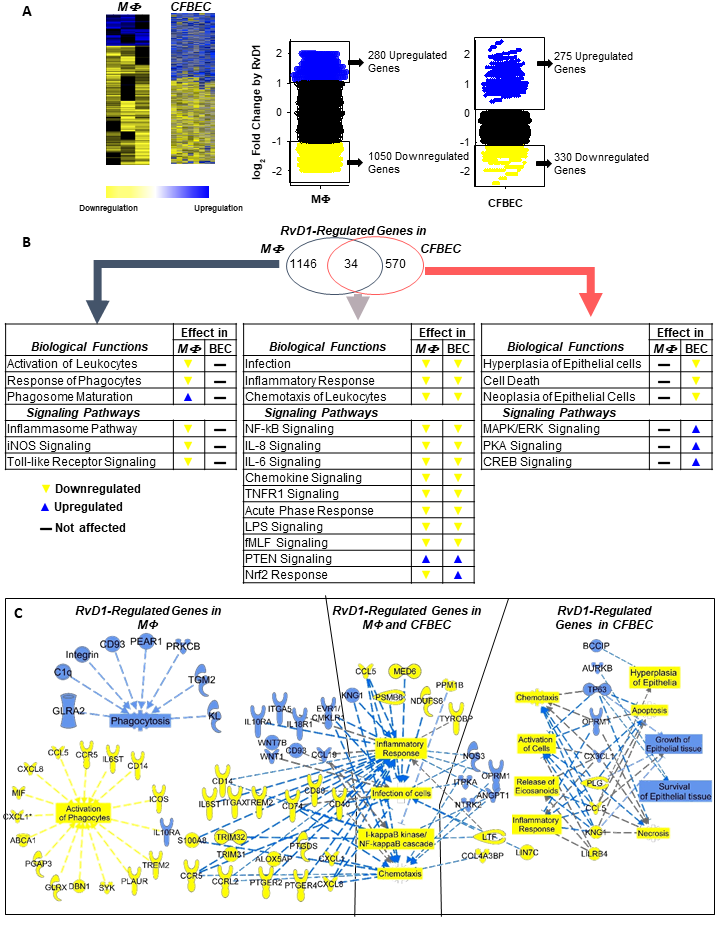
RvD1 regulates select genes related to microbial clearance and inflammatory signaling in CF macrophages and epithelial cells. Shown here are heat map view and scatter plots of expression patterns of genes differentially regulated by RvD1 in human homozygous ΔF508 macrophages (MΦ) and bronchial epithelial cells (CFBEC) infected with P. aeruginosa. B. IPA findings of biological functions associated with RvD1-regulated genes in MΦ and CFBEC.C. Top RvD1-regulated genes and associated functions identified by IPA. Blue symbols, upregulated genes; yellow symbols, downregulated genes; blue dotted lines, expression leading to activation; yellow dotted lines, expression leading to inhibition; gray dotted lines, expression leading to unpredictable effect of function; blue boxes, activated functions; yellow boxes, inhibited functions (Isopi et al., Front. Immunol., 2020). as it occurs in a non-CF setting (Codagnone et al., Mucosal Immunol., 2018). Resolvin D1 is organ protective in chronic P. aeruginosa infection and enhances non phlogistic clearance of P. aeruginosa and inflammatory cells by macrophages. Histopathology and semiquantitative scores of (A) inflammation and mucous metaplasia and (B) bronchiolar epithelial hyperplasia of lung sections collected at 21 DPI from infected mice receiving vehicle or RvD1 (100 ng/mouse) every 48 h from day 5 following inoculum. Photomicrographs are representative from 5 mice/group. Semiquantitative scores are mean ± SEM from 2 experiments with 5 mice/group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (Codagnone et al., Mucosal Immunol. 11:35-49. doi: 10.1038/mi.2017.36). These studies point out to SPM as innovative pro-resolutive therapeutic strategies for CF. Resolvin D1 and D2 reduce SARS-CoV-2 induced inflammatory signals in macrophages. The spike protein 1 S1 from SARS-CoV-2 triggers phlogistic responses in CF and non-CF MΦ encompassing activation of microRNAs and NF-κB-regulated chemokines and cytokines that drive further leukocyte functions. An unremitting MΦ activation can lead to excessive inflammation in patients with COVID-19. RvD1 and D2 RvD1 and D2 regulate select cytokines, chemokines, and microRNAs while enhancing MΦ phagocytosis of bacteria, thus proving important actions in SARS-CoV-2-driven inflammation and its resolution.READ MORE